This research was compiled by a financial researcher and fund manager who wishes to remain anonymous.
There are a few main reasons to be optimistic we should end lockdowns and get back to normal.
- We know who this coronavirus affects. The median age of death in almost all countries is over 80 with multiple existing conditions. We are failing to protect old people and are locking up the young and imposing social distancing when they have no risk of death. We can protect the vulnerable more intelligently.
- Most people have immunity due to cross reactivity and cross immunization. The human immune system is not completely helpless against this virus.
- Herd immunity levels are much lower than people think and the virus appears to follow a Gompertz curve, which correctly anticipates the virus fizzling out.
- In most countries, Covid deaths were 40-100% higher than a bad flu year.
The virus is bad but it is not the Spanish Flu and is most like the Hong Kong flu of 1968 and the Asian flu of 1957. They were bad, but we never shut the entire world down for those. Flus are deadly, the world is dangerous, and we will all eventually die. But we won’t all die form Covid.
Here is the complete collection of research and links categorized by subject. Examine the evidence for yourself.
Lockdowns are Terrible Ideas and Not Standard Practice
Those in favor of lockdown present a false dichotomy. Either we have a hard lockdown or we let the virus rip and kill everyone. That is hardly the case. Lockdowns and business closures are a sledgehammer that had no precedent in history and are not the way we have ever treated any virus or pandemic before. The costs are out of all proportion to the benefits. Many other strategies would be far better.
Here is a great case against lockdowns. How a Free Society Deals with Pandemics, According to Legendary Epidemiologist and Smallpox Eradicator Donald Henderson.
It concluded with this important paper.
There are no historical observations or scientific studies that support the confinement by quarantine of groups of possibly infected people for extended periods in order to slow the spread of influenza. A World Health Organization (WHO) Writing Group, after reviewing the literature and considering contemporary international experience, concluded that “forced isolation and quarantine are ineffective and impractical”. Despite this recommendation by experts, mandatory large-scale quarantine continues to be considered as an option by some authorities and government officials.
The interest in quarantine reflects the views and conditions prevalent more than 50 years ago, when much less was known about the epidemiology of infectious diseases and when there was far less international and domestic travel in a less densely populated world. It is difficult to identify circumstances in the past half-century when large-scale quarantine has been effectively used in the control of any disease.
The negative consequences of large-scale quarantine are so extreme (forced confinement of sick people with the well; complete restriction of movement of large populations; difficulty in getting critical supplies, medicines, and food to people inside the quarantine zone) that this mitigation measure should be eliminated from serious consideration.
No country had lockdowns in their playbook.
- For example, Canada’s pandemic guidelines concluded that restrictions on movement were “impractical if not impossible.”
- Also, according to the Wall Street Journal, “The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in its 2017 community mitigation guidelines for pandemic flu, didn’t recommend stay-at-home orders or closing nonessential businesses even for a flu as severe as the one a century ago.” Lockdowns were never part of the US response
- Lockdowns were never part of the WHO standard responses for pandemics. You can read here all their policies and how they rated the evidence for various measures.
- Most Asian countries like Taiwan, Japan and South Korea didn’t have lockdowns and had far better experiences than the European countries that did. Those who are sick are not sent home to infect family members and are separated, which is the exact opposite of European lockdowns.
Here is a very good read on the arguments against lockdowns. In most European countries, cases were already falling before the lockdowns as people were voluntarily taking preventive measures: social distancing, hand washing, wearing masks.
Many epidemiologists have been completely opposed to government plans and have in fact been right.
Only pro-lockdown scientists are amplified. Here is a good read on “the science“.
Here is Sunetra Gupta of Oxford, who opposed lockdowns are gave a great interview on UnHerd. Likewise, Martin Kuldorff, a Harvard epidemiologist who has been ignored. He’s argued in favor an age and risk-based approach.
But what do these people know about science? They’re only epidemiologists at Oxford and Harvard.
Lockdowns Were Not Needed or Effective
Lockdowns had almost no effect and the main determinants of death across countries was the percentage of people who were over 80, particularly men, and the % of people who are obese.
Here is a study in The Lancet showing lockdowns had no effect. The primary factors explaining deaths are obesity and age structure.
Here is a detailed study showing the virus behaved the same everywhere regardless of policy
Same is true on a county by county basis in the US, as you can read from this study. Whether a county had a lockdown has no effect on COVID-19 deaths; a non-effect that persists over time.
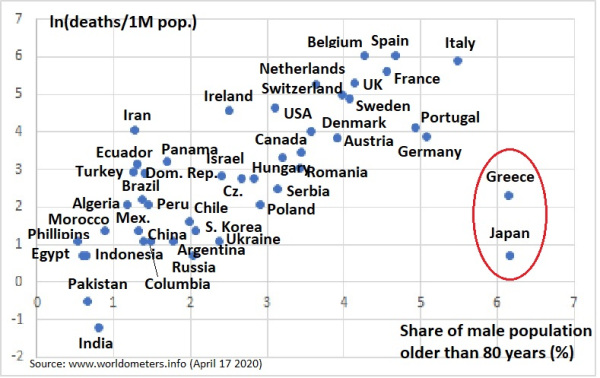
One of the biggest determinant of deaths from Covid related to the share of the population that was over 80, not to lockdowns. “Population age structures alone may account for four-fold variation in average regional infection-fatality ratios across Europe.”
and a useful visualization showing the high correlation between men over 80 as a percentage of the population vs death rates.
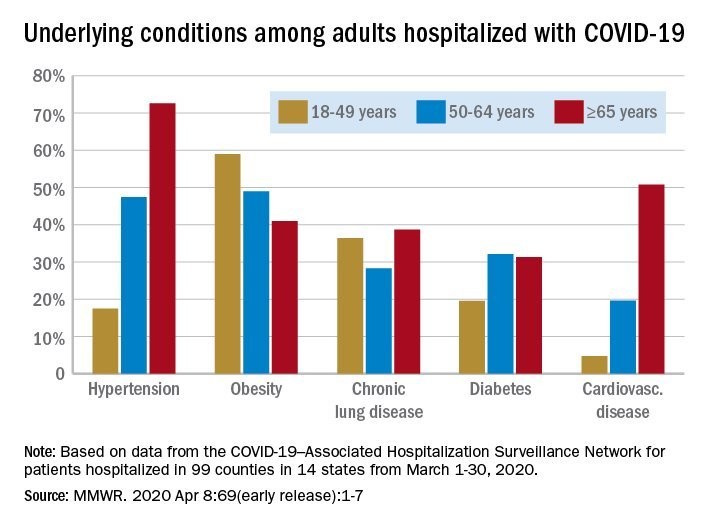
The other explainers for death rates are percentage of the population with hypertension:
and percentage of population with obesity/diabetes:
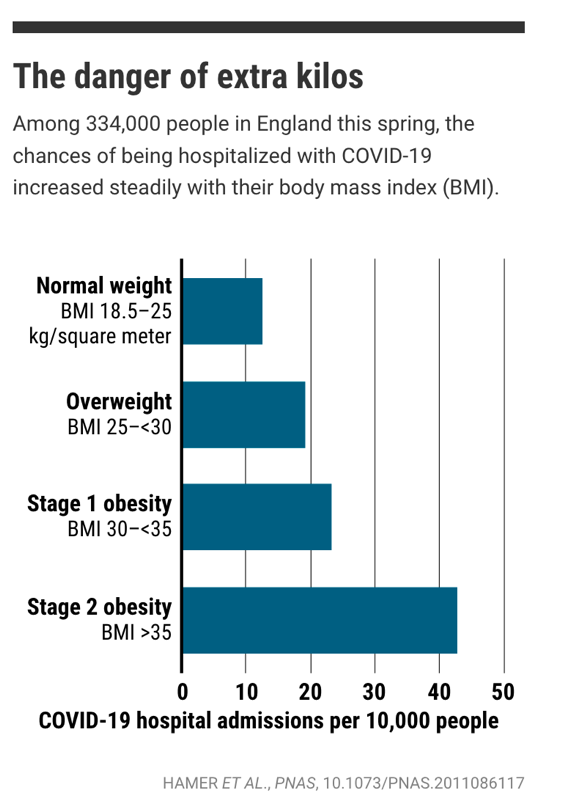
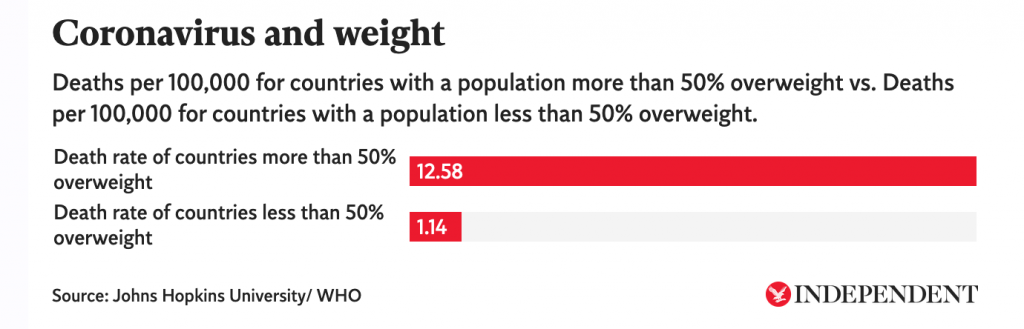
And a global look at obesity and death rates:
Deaths were falling before the lockdowns were imposed, as this study shows:
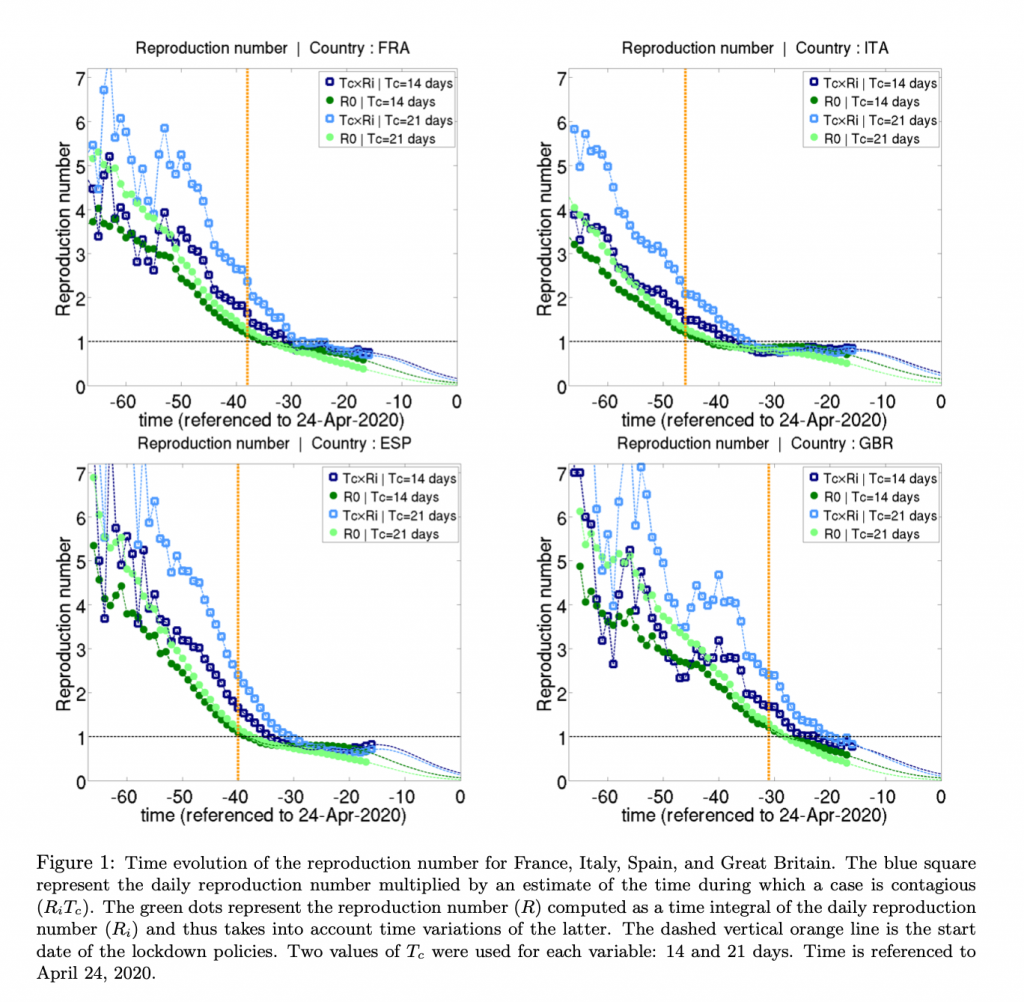
This is confirmed by many other papers, here and here. Here is a good article discussing these studies.
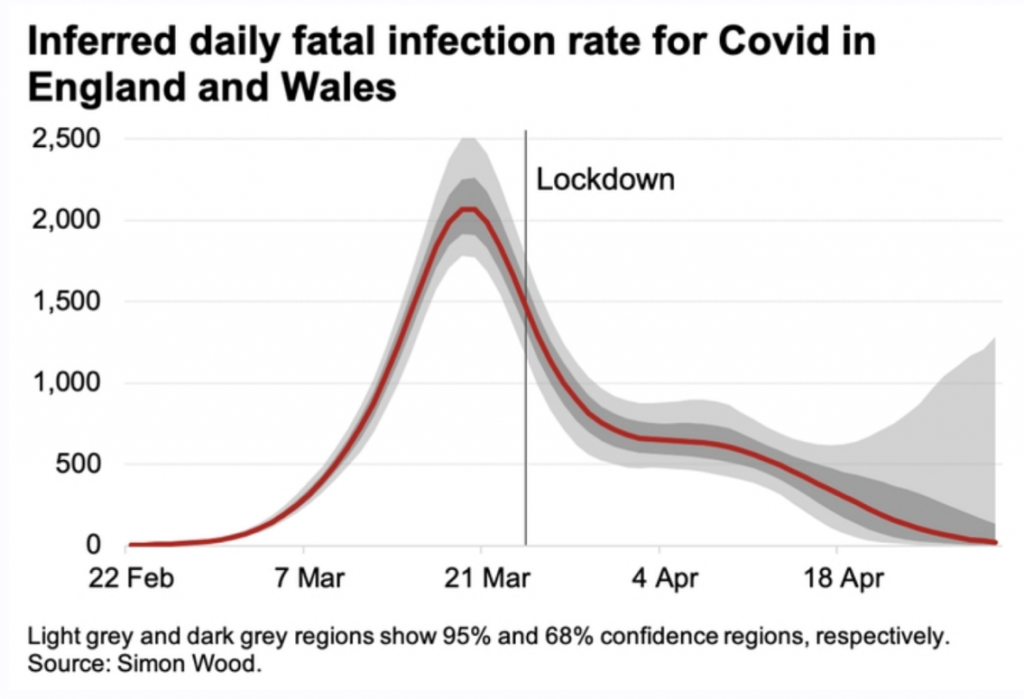
The same is true in other European countries. The decline in infections started before Germany even instituted lockdowns.
Bloomberg also found little correlation between severity of measures and death rates.
The Collateral Damage From Lockdowns is Vast and Will Kill Millions
Lockdowns are the moral equivalent of carpet bombing, ineffective with vast collateral damage.
Disruptions to food due to lockdowns may kill more from hunger than Covid.
Covid is not the only illness in the world and millions will die from interrupted care, for example from tuberculosis and HIV, as the New York Times reports.
“COVID-19 risks derailing all our efforts and taking us back to where we were 20 years ago,” said Dr. Pedro L. Alonso, the director of the World Health Organization’s global malaria program.
It’s not just that the coronavirus has diverted scientific attention from TB, H.I.V. and malaria. The lockdowns, particularly across parts of Africa, Asia and Latin America, have raised insurmountable barriers to patients who must travel to obtain diagnoses or drugs, according to interviews with more than two dozen public health officials, doctors and patients worldwide.
Unicef warns on the consequences of poverty and malnutrition for kids could harm millions.
According to a stark report published in Lancet Global Health journal on Wednesday, almost 1.2 million children could die in the next six months due to the disruption to health services and food supplies caused by the coronavirus pandemic.
The first famines of the coronavirus era are at the world’s doorstep, the UN warns.
COVID-19 could reverse decades of progress toward eliminating preventable child deaths, the WHO warns.
The Gates Foundation estimates that the response to Covid has set back vaccination 25 years.
Furthermore, there is good reason to believe that lockdowns increased deaths of the vulnerable and elderly.
This is true in much of the world. Here is a study looking at how lockdowns drove excess deaths for non-Covid illnesses.
Interrupting medical care kills people. More people died in Denver of unattended heart attacks during lockdown than from Covid.
New cancer diagnoses collapsed in the United States as the coronavirus pandemic first hit. Almost all diagnoses collapsed in the UK as well.
And same was true for heart attacks and strokes in the NHS in the UK.
Analysis of NHS data reveals the deadly consequences of the government’s messaging to “stay at home, save lives, protect the NHS”. During the lockdown, there was a near 50 per cent decline in admissions for heart attacks. The risks of COVID-19 outweighed the risk of seeking NHS care despite worsening symptoms for many people: 40 per cent more people died from lower-risk treatable heart attacks than usual. For strokes, the situation is further exacerbated by living alone and not having visitors as 98% of emergency calls for strokes are made by someone else.
The economic damage is also horrific.
The World Bank estimates over 71 million will be plunged into extreme poverty due to lockdowns/quarantines
The United Nations has warned that response to Covid is reversing decades of gains in poverty, healthcare and disease
More Than Half of US Business Closures Permanent, Yelp Says. Half of black businesses in the US have been wiped out.
The Virus is Not at all Deadly For Those Under 55
One paper looking at Infection fatality rates by age summarized it well.
“The estimated IFR is close to zero for younger adults but rises exponentially with age, reaching about 0.3% for ages 50-59, 1.3% for ages 60-69, 4% for ages 70-79, 10% for ages 80-89.”
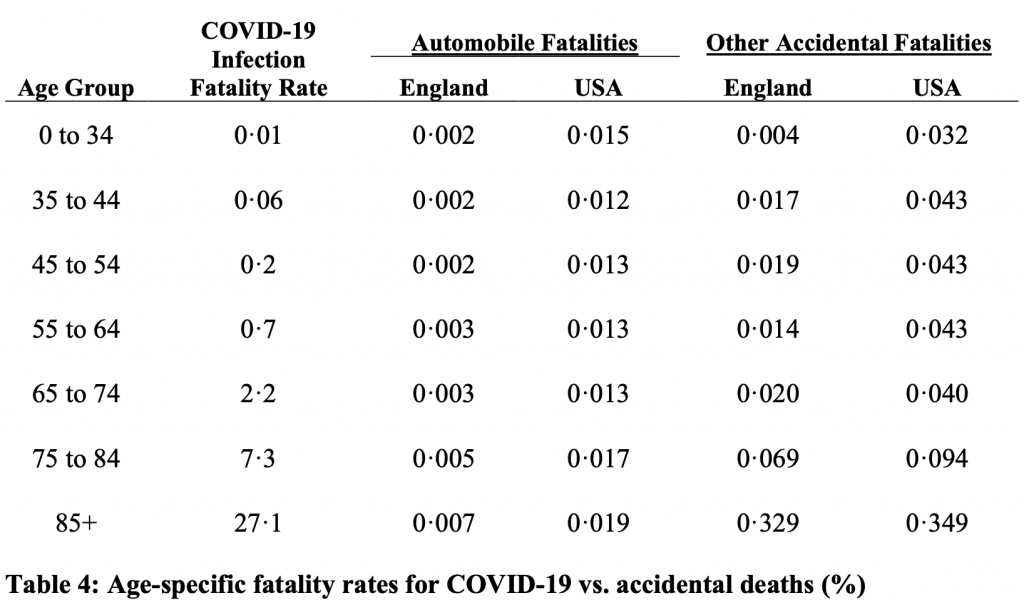
In fact, the distribution of risk matches “normal” risk of death by age.
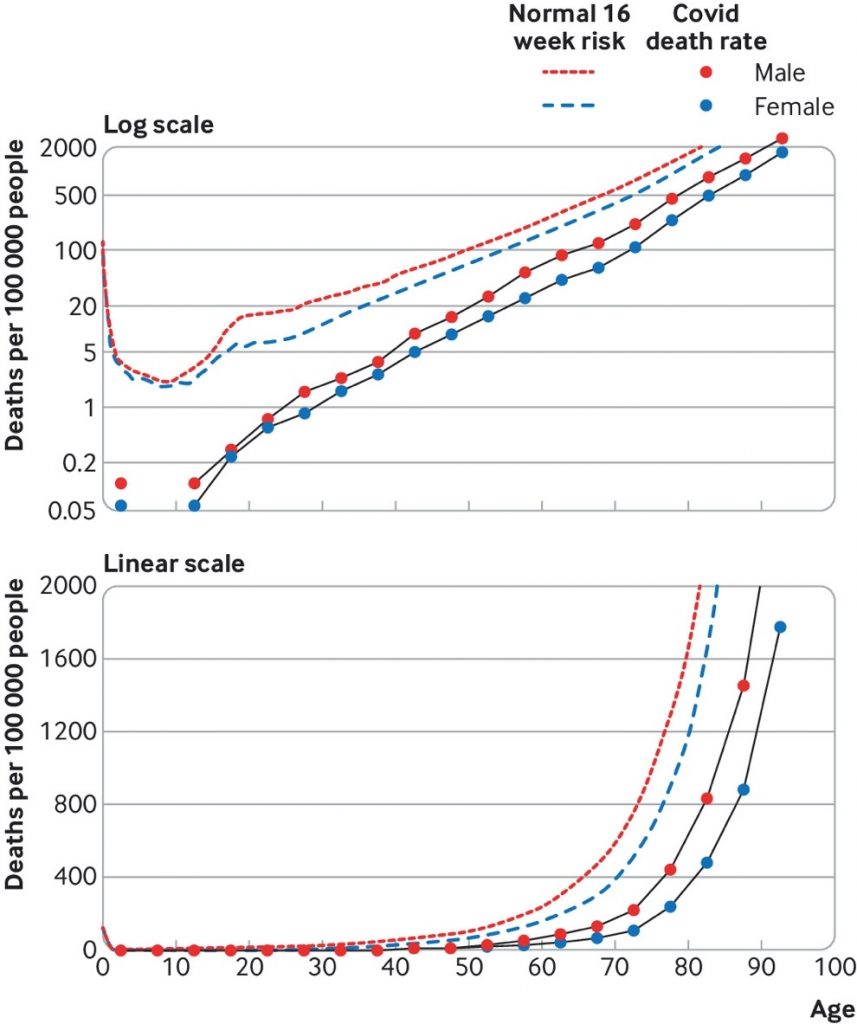
The Infection Fatality Rate is far lower than initially estimated.
Here is the link to all the studies on infection fatality rates for Covid. The evidence is overwhelming.
The virus is not at all deadly to younger people. Here are death breakdowns by age group in the US and Europe
And from the Oxford for Evidence Based Medicine (scroll to bottom).
The median age for death in most countries is over 80 and the average person has multiple pre-existing conditions.
In Italy the median age was over 80 and 96% of people had existing conditions.
Spain showed exactly the same pattern.
US – Median death age from Covid in the US was 80 years.
That is slightly above the average life expectancy overall.
In many countries the median age of death is above life expectancy, i.e. people had already lived longer than the average person.
Covid is not at all deadly for those without significant co-morbidities.
Table 3 of the CDC’s data on deaths between 2/1 and 8/22 2020 says directly that only 6% of the 161,392 reported COVID deaths were listed as COVID-19 alone, just 9,684. All other US deaths had, on average, 2.6 additional conditions.
Population-level COVID-19 mortality risk for non-elderly individuals overall and for non-elderly individuals without underlying diseases in pandemic epicenters was very low.
The COVID-19 mortality rate in people <65 years old during the period of fatalities from the epidemic was equivalent to the mortality rate from driving between 4 and 82 miles per day for 13 countries and 5 states, and was higher (equivalent to the mortality rate from driving 106–483 miles per day) for 8 other states and the UK. People <65 years old without underlying predisposing conditions accounted for only 0.7–3.6% of all COVID-19 deaths in France, Italy, Netherlands, Sweden, Georgia, and New York City and 17.7% in Mexico.
People <65 years old have very small risks of COVID-19 death even in pandemic epicenters and deaths for people <65 years without underlying predisposing conditions are remarkably uncommon. Strategies focusing specifically on protecting high-risk elderly individuals should be considered in managing the pandemic.
Most people had hypertension as a co-morbidity. People with hypertension have a lower life expectancy with or without Covid
Irrespective of sex 50-year-old hypertensives compared with normotensives had a shorter life expectancy a shorter life expectancy free of cardiovascular disease myocardial infarction and stroke and a longer life expectancy lived with these diseases. Normotensive men (22% of men) survived 7.2 years (95% confidence interval, 5.6 to 9.0) longer without cardiovascular disease compared with hypertensives and spent 2.1 (0.9 to 3.4) fewer years of life with cardiovascular disease. Similar differences were observed in women…. Compared with hypertensives total life expectancy was 5.1 and 4.9 years longer for normotensive men and women respectively. Increased blood pressure in adulthood is associated with large reductions in life expectancy and more years lived with cardiovascular disease. This effect is larger than estimated previously and affects both sexes similarly. Our findings underline the tremendous importance of preventing high blood pressure and its consequences in the population.
The same is true for diabetes. Diabetes significantly shortens people’s lives with or without Covid.
According to the reports of Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA); men with type 1 diabetes have a shortened lifespan of 11 years than normal men. Women with the condition have their lives cut short by 13 years.
A 2010 report by the Diabetes UK claims that type 2 diabetes reduces the lifespan by 10 years. A 2012 Canadian study claimed that women aged over 55 years with type 2 diabetes lost on an average of 6 years while men lost 5.
The probability of dying under 65 without co-morbidities is extremely low to non-existent.
It is far more sensible to protect the vulnerable than close society.
Children Do Not Spread the Virus and are Not at Risk
Sweden kept their schools open and not a single child died from Covid of over 1.8 million kids.
Closure or not of schools has had little if any impact on the number of laboratory confirmed cases in school aged children in Finland and Sweden. Children are more likely to die from flu than Covid.
No transmission from children in Greece. Transmission dynamics of SARS‐CoV‐2 within families with children in Greece: a study of 23 clusters.
From the Official Journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics. COVID-19 Transmission and Children: The Child Is Not to Blame.
No evidence of secondary transmission of COVID-19 from children attending school in Ireland 2020.
German study shows low coronavirus infection rates in schools.
Children are not COVID-19 super spreaders: time to go back to school, from the BMJ.
The Royal College of Paediatricans and Child Health review of the evidence shows children don’t transmit the virus.
A CDC study showed very limited transmission in childcare settings.
Here are government reports all showing children are not the main source of transmission from the EU and Norway and Netherlands. In fact, children are more likely to be hit by lightning than die from Covid. The evidence is overwhelming.
Public Policy Response to Age Differences
Strategies targeted by age are likely to be much more useful at reaching herd immunity with less damage.
An age and risk based approach is by far the most sensible and what is advocated by epidemiologists like Martin Kulldorff from Harvard. Here is an article he wrote in The Spectator and LinkedIn. Here is a podcast he did. And here is another article in Contagion. In fact, he argues that delaying herd immunity is costing lives. The current lockdown is protecting the healthy instead of the vulnerable. He also wrote a very good piece on the proper response. Given the age differences in risk, policy responses should be age-specific.
The irony of shutting schools and universities and creating unemployment is that the very young and very old mix more than ever before. That is the unintended consequence of the response to the virus. We have the worst of all worlds.
Elderly are Most Vulnerable, 50–60% of All Deaths Were Care Home Deaths
In most countries between 50-60% of deaths from Covid are from care homes. In some countries and states it is as high as 80%. What is extraordinary, though, is that this is largely a self-inflicted wound. Many infected old people were sent away from hospitals to care homes to infect others. This is true in the UK, NY and California.
This is by far the best site on all issues relating to care homes internationally. It shows percentage of all Covid deaths are 50-60% for almost all countries. Here is their main report with extensive data by country and 50-60% of deaths on average
In the first few months of the pandemic, 42% Of U.S. Deaths Are From 0.6% Of The Population in Care homes. As of September, according to the New York Times, 40% of US deaths were in care homes.
And you can read more here. The Real Pandemic Was a Nursing Home Problem. Here is a Wall Street Journal article with more data from US nursing homes regarding deaths
Some countries and states have 70-80% of all deaths in care homes.
- Canada 82%
- Northern Ireland 80%
- New Jersey at 76%
- Sweden 70% (Very few non-elderly died in Sweden. This is a very good read on the problems of Swedish care homes.)
- Ohio 70%
- Pennsylvania 70%
- Arizona 70%
- Florida 70%
This is an extraordinary resource that shows care home deaths in the US. In some states up to 10% of all nursing home residents died. It is likely care home deaths are understated and hospital overstated. For example, 15% of hospital deaths in the UK were actually care home patients who went to the hospital according to the ONS. While Covid deaths are horrible, it is worth considering what life expectancy without Covid would be in care homes. Even without Covid, life expectancy is extremely short in care homes. You can read here and here. The length of stay data are striking:
- The median length of stay in a nursing home before death was 5 months
- 65% died within 1 year of nursing home admission
- 53% died within 6 months of nursing home admission
The finding of median death in nursing homes being less than one year is confirmed in other studies. Those placed in care homes are often in worse health. Caregivers who institutionalise their relatives are substantially more likely to become bereaved than those whose relatives continue to reside at home. The zero-order odds of patient death more than double following admission to a nursing home. Instead of locking down children and young people, it might make more sense to protect the elderly.
Politicians Caused Care Home Deaths Through Bad Policy
In many states, infected old people were sent into care homes to infect others. Here was New York in April. Here is New Jersey, Pennsylvania and the Northeast. Here is the United Kingdom. This was not only done early in the crisis but as late as May when it was clear that care homes were hotspots. Governor Gavin Newsom ordered care homes take in infected residents in May. This is packed with links and further reading.
The only correct historical analogy is the Siege of Caffa where Tartars threw infected bodies of the dead over city walls to spread the disease.
Why Herd Immunity Thresholds Are Lower Than Assumed
It is highly likely that herd immunity for Covid is at much lower levels than people think. The main reasons are 1) populations are not homogenous i.e. we have different age groups with different susceptibilities, and 2) we all don’t mix randomly, i.e. most people live boring lives and see the same people every day. Simply put, heterogeneity and non-random mixing massively reduce the threshold for herd immunity.
- Here is a good accessible explanation of why herd immunity levels are much lower than expected for many diseases.
- Here is an accessible introduction to the question of why estimating herd immunity isn’t straightforward or high as many articles claim.
- Here is a detailed blog post with links to studies on how the herd immunity threshold is lower than people think. And a slightly more technical explanation and another one
- Here is a discussion of why immunity levels are lower than assumed.
- Here is a very good read from the British Medical Journal making the case.
- Here is an academic paper on why Covid will have lower herd immunity thresholds. Here is a great podcast with the author who specializes in modeling herd immunity. She wrote a paper arguing that herd immunity is closer to 20% for Covid due to high heterogeneity of population and low susceptibility. So far, given how the virus is fizzling out almost everywhere there is a first wave, and the results of antibody tests, it looks like she’s right. It is worth a listen.
- Here is a paper noting that Herd Immunity Thresholds are much lower in Sweden. Given they had no lockdown and now have zero deaths or people in ICUs, this is the explanation.
- Another paper arguing, the disease-induced herd immunity level for COVID-19 is substantially lower than assumed
- Another paper showing that most first wave Covid locations are at herd immunity based on heterogeneous susceptibility
- Heterogenous transmission is likely why we have more cases with lower deaths, as this paper shows. The virus spreads in less susceptible people
- The reason care homes are so vulnerable is that populations are not heterogenous, as this paper shows.
- Here is a broader read on heterogeneity of populations and the effectiveness of vaccines, which touches on the same issues of heterogeneity of susceptibility.
- Here is a discussion of the role of non-random mixing from a few months ago, which was much more accurate than the early estimates of vast deaths.
It is highly unlikely a majority of a population will not get Covid. Much lower effective herd immunization thresholds fit what we see every year with flus, even bad ones.
- According to the WHO about 15% of people get flu a year.
- According to the CDC about 3-11%% of the population gets the flu any year, and that includes asymptomatic people.
- A 2018 CDC study published in Clinical Infectious Diseases looked at the percentage of the U.S. population who were sickened by flu using two different methods and compared the findings. Both methods had similar findings, which suggested that on average, about 8% of the U.S. population gets sick from flu each season, with a range of between 3% and 11%, depending on the season.
The last pandemic was H1N1 and that peaked at 20-24% of the global population during the first year. That is one the very high end.
If you want further background reading, here is a terrific overview of herd immunity.
Most People Have Immunity and a Defence Response T-Cell Cross Reactivity and Cross Immunization
Early on, many politicians and scientists assumed Covid was very deadly because we had no existing immunity to Covid. This is not true. Many people do have some existing immunity to Covid. This comes from T-cells, which provide us with an immune response.
- A study of patients and their families shows that an unexpected six out of eight family members who caught the virus at home had T-cell responses but no detectable antibodies. Intrafamilial Exposure to SARS-CoV-2 Induces Cellular Immune Response without Seroconversion
- Important peer-reviewed paper in Nature about the likely immunity to COVID-19 conferred by T cells ‘SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell immunity in cases of COVID-19 and SARS, and uninfected controls‘
- Here is a paper on cross reactivity in Cell journal indicating 40-50% cross reactivity
- Here is a paper on T-cell response to #SARSCoV2 was observed in 81% of uninfected individuals. This immune response was caused by prior exposure to ‘common cold’ coronaviruses.
- Here is a study done in Sweden showing 30% of blood donors had T-cell responses
- Here is very good piece explaining cross reactivity and why kids don’t get it and another and another
- Here is a brief discussion of another paper and the paper
- And another on SARS-1 providing cross reactivity
Cross reactivity is likely to come from other vaccines people already have. There is a strong relationship between MMR vaccine and age-stratified COVID fatality rates. Here is the study. MMR Vaccine Appears to Confer Strong Protection from COVID-19: Few Deaths from SARS-CoV-2 in Highly Vaccinated Populations.
Here is good summary of the issue of existing immunity and cross-reactivity for non-scientists in the Guardian and American Conservative.
In this interview, Sunetra Gupta from Oxford University hits on cross reactivity but doesn’t go into technical details. As she sees it, the antibody studies, although useful, do not indicate the true level of exposure or level of immunity. First, many of the antibody tests are “extremely unreliable” and rely on hard-to-achieve representative groups. But more important, many people who have been exposed to the virus will have other kinds of immunity that don’t show up on antibody tests – either for genetic reasons or the result of pre-existing immunities to related coronaviruses such as the common cold.
Karl Friston has noted that up to 80% not even susceptible to COVID-19.
The Virus Naturally Fizzles Out and Most States/Regions Follow the Gompertz Curve
We know that the virus naturally fizzles out because we have Sweden and Manaus in Brazil and other natural experiments where there were no lockdowns. In Manaus, there were no distancing measures either, and the virus fizzled out.
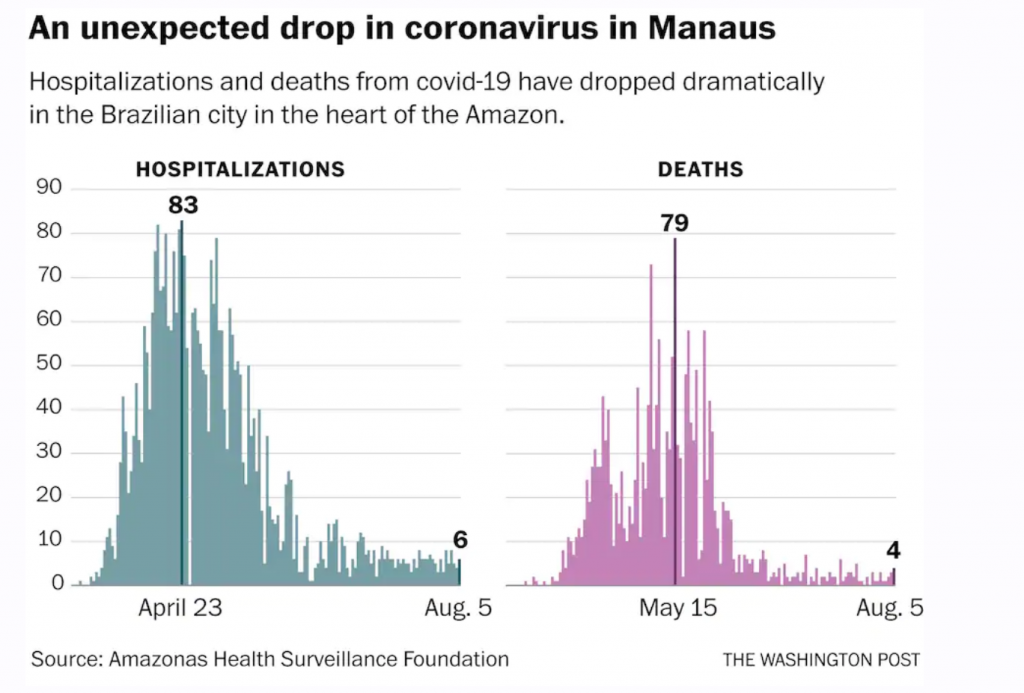
In Sweden you can see deaths and ICU cases are in the single digits They had 5,800 deaths (70% in care homes, which they could have handled better) and today deaths and hospitalizations are in the single digits and zero most days. Their policy worked.
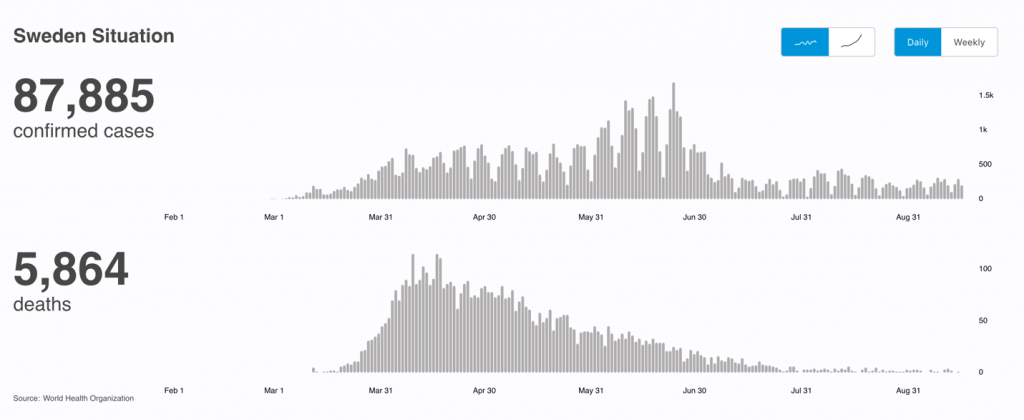
Believe it or not, Sweden, where everyone was supposed to die due to no lockdowns, has had worse months of deaths from flu in the last 30 years in 1993 and 2000.
All of this explains stories like this where experts wonder about why the virus fizzles out at a certain point. A curious pattern in coronavirus infection rate emerges, hinting it can ‘burn out’ at a certain point.
Farr’s law explains why viruses don’t grow exponentially and infect everyone.
Nobel prize winner Michael Levitt has written a paper on the math behind how viruses fizzle out, which fits much lower herd immunity levels. Here is an explanation in plain English.
Interestingly, there were a few papers from China and Spain (in Spanish, but you can use Google or Bing translator) that correctly predicted the peaks and end of the virus and number of deaths using Gompertz curves as far back as March. There are specific reasons why the virus follows a Gompertz function.
While some countries look like they’re having second waves or not following the Gompertz curve, the truth is they are. For example, Brazil is actually many big cities that have their own curves.
And deaths are following the Gompertz curve by city, so see Rio, for example.
All European cases are now close to zero and all curves look the same by country, and for Europe as a whole.
UK is at zero and looks exactly the same:
The same is true in the US. Early states like NY and NJ have almost no deaths and look like Europe. Later states that had no first wave looked like Eastern Europe. It is now peaking and turning down.
The Virus is Fizzling Out
Notice in every single Western European country the virus has fizzled out and deaths are running below one per million per day and in most countries are near zero.
Here is Europe’s aggregate chart:
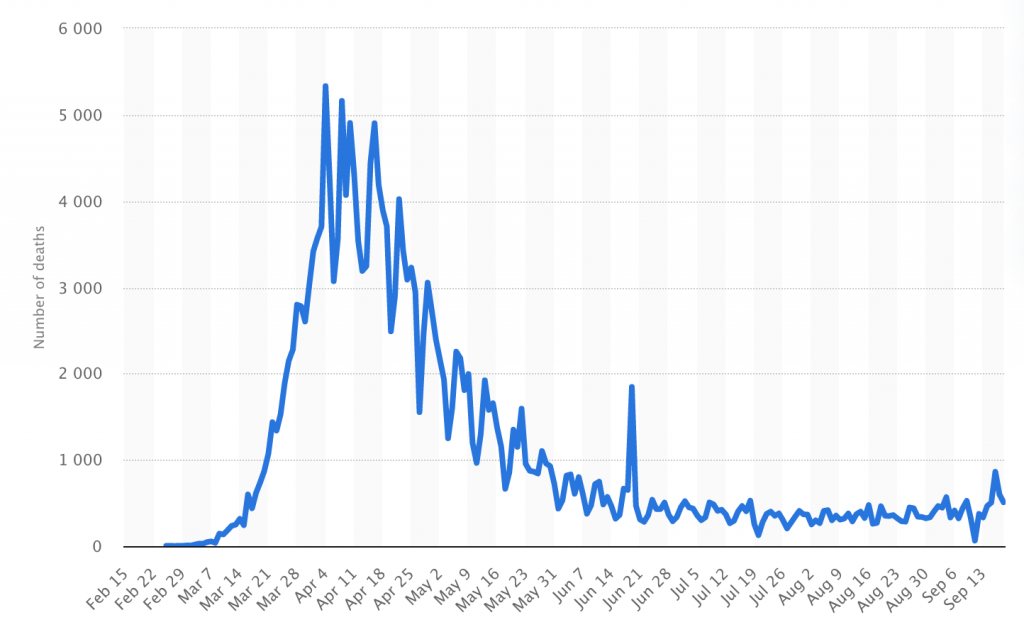
Today everyone is worried about cases, but there are almost no deaths and it is all due to more testing.
Despite the media’s breathless reporting of deaths, in most European countries, Covid deaths were 40-100% worse than a bad flu year (see below on all links for data).
The hotspots in the sunbelt saw deaths peak in July. Hospitalisations peaked in mid-July in all hotspots as well as visits for influenza, pneumonia and Covid according to CDC:
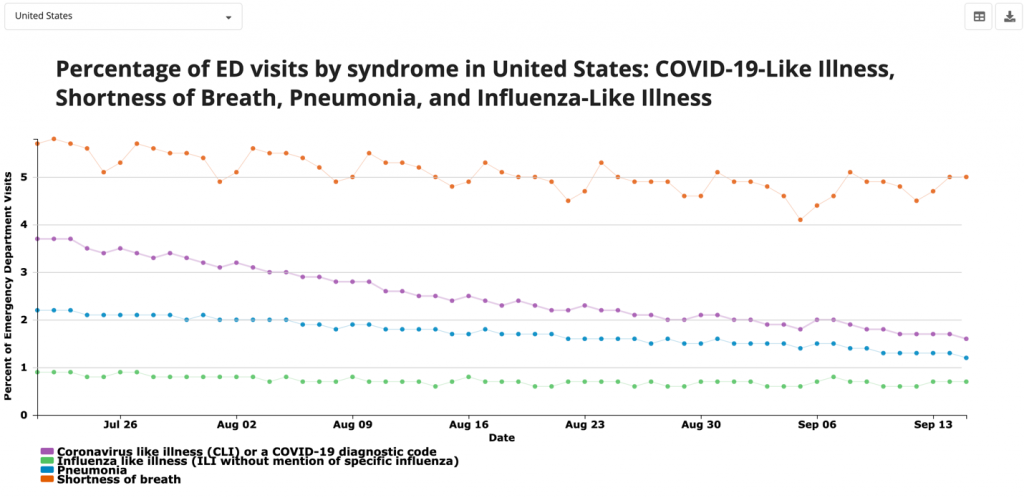
You can see the trend in deaths has been falling:
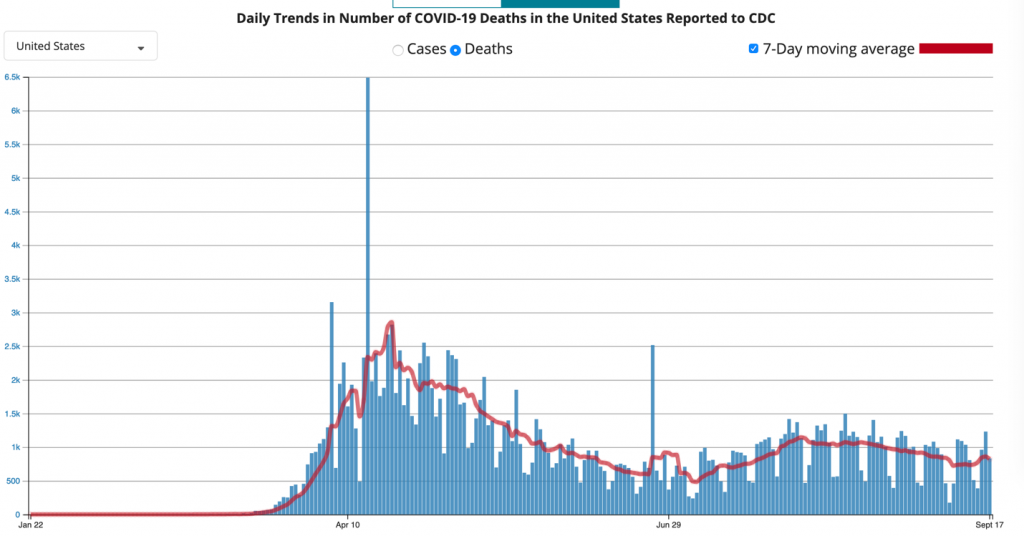
Here is Arizona with all trends in the right direction with fall in hospitalizations, ICUs and even deaths:
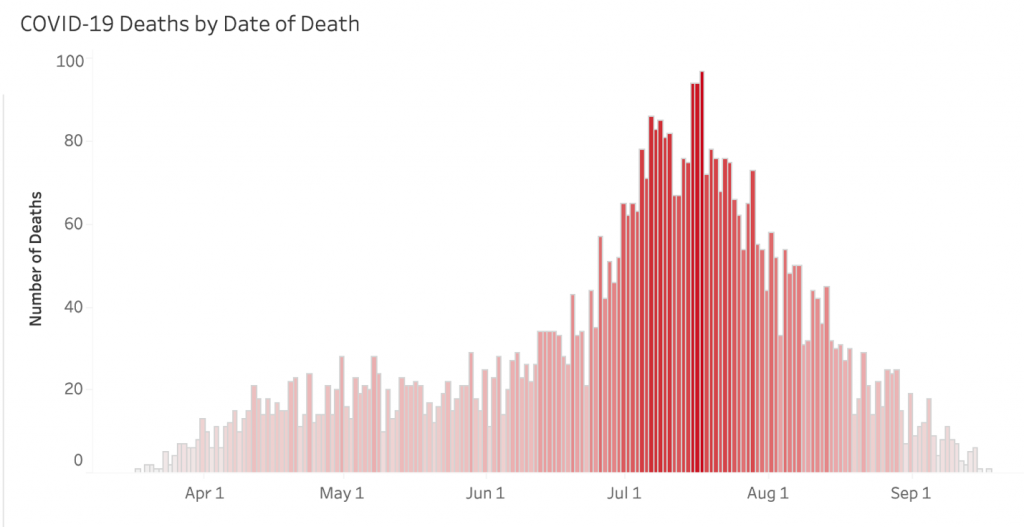
Florida is the same.
Texas is the same.
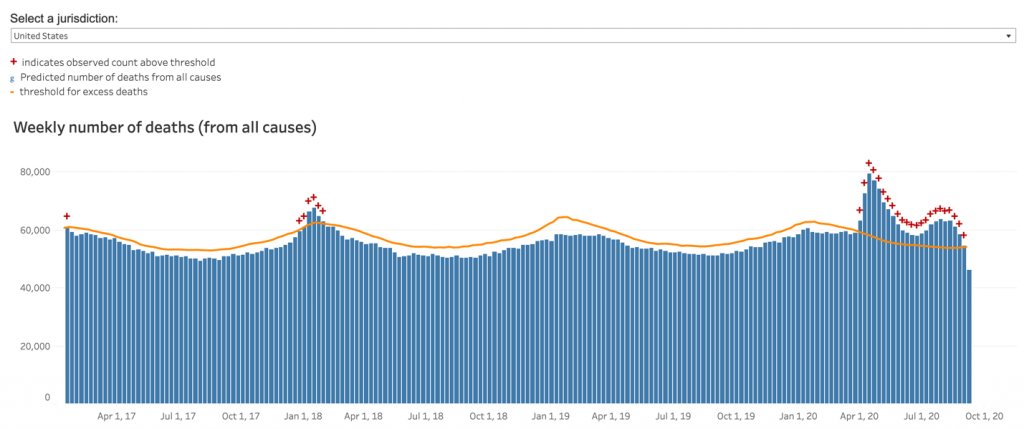
Believe it or not, in the US excess mortality is now almost back to normal.
While some countries look like they’re having second waves or not following the Gompertz curve and fizzling out, the truth is they are. For example, Brazil is actually many big cities that have their own curves. And deaths are following the Gompertz curve by city, so see Rio de Janeiro, for example.
Putting Covid in Perspective vs the Flu Globally
Currently, global deaths are 800,000 from Covid.
Globally, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that the flu kills 290,000 to 650,000 people per year.
So Covid is running a little over the upper end of world flu deaths annually.
Europe
180,000 people have died in all of Western Europe from Covid. Here is a study of 2017/18 season. It states that 152,000 people died during flu season from flu and unknown pathogens.
The impact of the 2017/18 influenza epidemic on mortality was similar to that of the previous influenza A(H3N2) dominated seasons in 2014/15 and 2016/17. The European number of deaths attributable to influenza was estimated to be 152 thousand persons. We found a lower influenza-attributable mortality compared to excess mortality, which may indicated that other circulating pathogens might also have contributed to the all-cause excess mortality.
See the European flu monitoring site showing flu vs Covid. It isn’t twice as bad as previous bad flu seasons 2014/15 and 2017/18
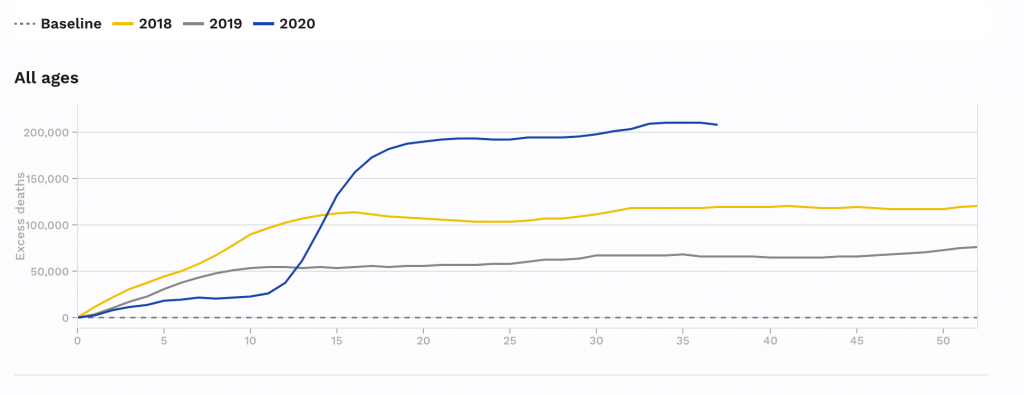
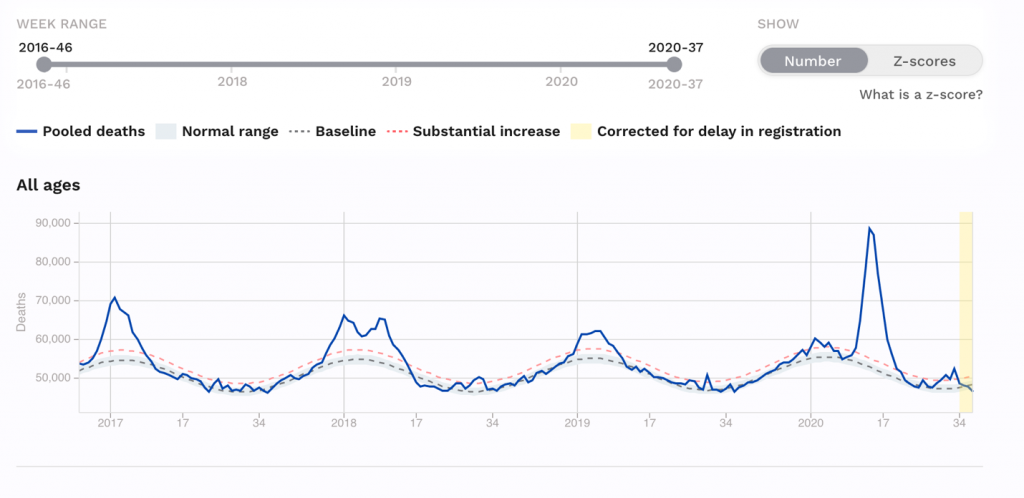
Italy had 35,000 Covid deaths.
But Italy always has more deaths from influenza than other European countries.
It had excess deaths of 7,027 20,259 15,801 and 24,981 attributable to influenza epidemics in the 2013/14 2014/15 2015/16 and 2016/17 respectively.
That means Covid was only 40% worse than their worst flu year in the last five years.
The UK has had ~46,000 deaths from Covid.
For some perspective, there were 28,000 and 26,000 deaths from influenza in the UK in 2014 and 2017.
So the end result is the virus is about 40% worse than a bad flu year.
France has had 30,000 Covid deaths.
That is only 60% worse than the 2014/15 flu season in France with 18,300 deaths.
Spain has had 28,000 Covid deaths.
But it has had about 15,000 deaths from flu in previous flu seasons, notably 2014/15. ”Using population models, it has been estimated that in the last two seasons, the flu may have been responsible for up to 15,000 deaths attributable to this disease.”
The Instituto Nacional de Estadistica says 15,000 for last two seasons, so that is a bad year.
So Covid is basically twice as bad as a bad flu season in Spain.
The US has had 190,000 deaths.
The flu season in 2017-18 had a median estimate of 61,000 deaths, but upper bound of the estimate is 95,000 deaths.
The 2014-15 had 64,000 as top estimate for flu deaths.
So Covid is roughly 60%-100% worse than the worst flu season we’ve had in the US.
Another issue that is rarely mentioned is that Covid deaths and hospitalizations have been inflated. Here is the Irish Government’s analysis of Covid deaths. Many people had the virus but did not die of Covid.
Likewise, Britain’s official death toll from the COVID-19 pandemic was lowered by over 5,000.
Sites avoiding groupthink
They are worth bookmarking










Donate
We depend on your donations to keep this site going. Please give what you can.
Donate TodayComment on this Article
You’ll need to set up an account to comment if you don’t already have one. We ask for a minimum donation of £5 if you'd like to make a comment or post in our Forums.
Sign UpEffects of False Positive Results
Next PostLatest News